
- Home
- All Posts
- Flow Battery
- Vanadium Redox Flow Battery
- Basis of Vanadium Redox Flow Battery
Blog

Basis of Vanadium Redox Flow Battery
Principle of Vanadium Redox Flow Battery
The vanadium redox flow battery(VRFB) converts chemical energy to electrical energy, and vice versa. V-flow battery employs vanadium ions in different oxidation states to store chemical potential energy. Vanadium-based electrolyte solutions stored in separate tanks that are pumped via manifolds through half-cells separated by a membran. In the half-cells the electrochemical reactions take place as soon as electrolytes flow past the membranes. The reduction or oxidation thus leads to the charging or discharging of the battery.
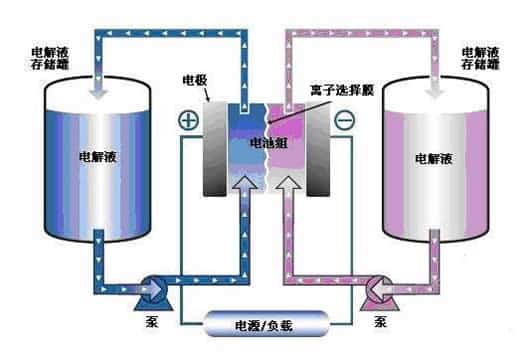
It can be seen from the above figure that the vanadium redox flow battery includes two electrolyte storage tanks with vanadium ions in different oxidation states, the positive electrode V (IV) / V (V) and the negative electrode V (II) / V (III). The electrolyte is circulated between the storage tank and battery stack by the pump. The stack includes several battery packs, each of which has two half cells, and separated by a proton exchange membrane. In the half cell, the electrochemical reaction is carried out on the carbon plate electrode to generate electric current for charging and discharging the battery.
Features of all-vanadium redox flow battery
1) Good safety: the active material for VRFB energy storage system is vanadium ion solution, which runs under normal temperature and pressure, no combustion will occur. After a long-time operation, even if the ion exchange membrane is broken and the positive and negative active materials are mixed together, explosion and combustion will still not occur. During the operation of the system, the electrolyte circulates between the stack and the electrolyte storage tank, the heat caused by the stack can be effectively discharged, the heat management is simple. The technical characteristics of the VRFB system ensure good consistency between the single cells, eliminate safety problems caused by poor consistency just like lithium-ion batteries.
2) Long cycle life: the charging and discharging cycle life of all-vanadium redox flow battery can reach more than 13000 times, and the calendar life is more than 15 years. Since vanadium ion exists in the fluid electrolyte, during the redox reaction, vanadium ion only produce valence change rather than phase change, and the electrode material does not participate in the reaction, so the battery life is pretty long. The 25kW VRFB module manufactured by Sumitomo of Japan has been operated in the laboratory, and the number of charge and discharge cycles exceeds 16000. The 4MW/6MWh flow battery system used with the wind farm has achieved 270000 charge and discharge cycles in 3 years of application. In 1MW/5MWh VRFB system, the cost of electrolyte accounts for about 45% of the whole cost. The cost performance ratio in whole life is high because the electrolyte can be recycled.
3) Good charge and discharge performance: All vanadium flow battery system can quickly charge and discharge while will not affect the service life of the battery, and the uniformity of each single cell is good. In addition, vanadium ion has high electrochemical reversibility and small electrochemical polarization, so it’s very suitable for high current charge and discharge. Comparing to other battery technologie, VRFB is more proper for operation under the extreme working conditions such as such as over charge, under charge and local SOC interval.
4) Independent design of power and capacity: one of the significant advantages of Vanadium flow battery system is that power and capacity are independent of each other. The power of VRFB is determined by the specification and quantity of the stack, and the capacity is determined by the concentration and volume of the electrolyte. Therefore, the expansion of power can be realized by increasing the power of the stack or adding number of stacks, and the improvement of capacity can be realized by increasing the volume of electrolyte. Independently scalable in power and capacity, lead to flexible design.
5) Environment friendly: the electrolyte solution of all vanadium flow battery can be recycled. Among the key materials of battery stack, the electrode material is carbon felt, the bipolar plate is carbon plastic, the collector plate is copper plate, the end plate is aluminum alloy plate or cast ironplate, the electrolyte transmission pipe is based on engineering plastic material. Rich in material sources, mature processing technology, easy for recycling, environmental friendly during their whole life cycle.
Problems in development of VRFB system
1) Low energy density and large volume. The battery system equipped with a large quantity of auxiliary components such as pipelines, valves, electrolyte circulation pumps and heat exchangers, which makes the flow battery complicated and puts forward higher requirements for the reliability of the battery system.
2) Ion exchange membrane technology. Ion exchange membrane can affect the ion permeability between positive and negative electrolyte, thus affect the energy efficiency and battery life of flow battery. It’s necessary to research and develop proton-exchange membrane with high selectivity and high conductivity for energy storage system.
3) High concentration and high stability electrolyte preparation technology. Previously, the cost of electrolyte is accounted for nearly 50% of the total cost. At present, due to the reduction of battery cost, the proportion of electrolyte cost is larger.
Development prospect of Vanadium battery in China
1) Over the past 15 years, more than 50 projects around the world have verified the mature commercial application of all vanadium flow battery. The characteristics of long life, repeatable discharge and high reliability, can fully meet the requirements of building a strong power grid in China.
2) Through transnational integration and independent research and development, most of the key patents of the global vanadium battery core technology are mastered by Chinese companies. Since the 1990s, many domestic research institutions and companies have carried out research in this field and accumulated a lot of professional talents.
3) China has rich vanadium resources and relatively low-cost manufacturing capacity, which provides China with the basic conditions for large-scale production of vanadium batteries.
4) Considering the development of renewable energy and the demands for environmental improvement, all vanadium redox flow battery has a broad development prospect in China.
About Mr. Zhou
Search
Recent Posts
-
Manufacturing Process of Ca... 11/28/2024
-
Application of Flexible Gra... 05/14/2024
-
PEM Water Electrolysis for ... 04/12/2024
-
Application of Bipolar Memb... 01/09/2024
-
Membrane Electrode Assembly... 11/27/2023
Categories
- All Posts (24)
- Flow Battery (11)
- Battery Material (20)
- Bipolar Plate (13)
- Membrane (3)
- Felt Electrode (1)
- MEA (3)
- Fuel Cell (5)
Contact Info.
Recent Post
-
Manufacturing Process of Ca... 11/28/2024
-
Application of Flexible Gra... 05/14/2024
-
PEM Water Electrolysis for ... 04/12/2024
-
Application of Bipolar Memb... 01/09/2024
-
Membrane Electrode Assembly... 11/27/2023


